In the field of intelligent manufacturing and warehousing logistics, the demand for handling robots is increasing year by year. The types of robots (AGVs) vary widely, and how to choose to become a headache for the demand side.
This article will compare the common industrial-grade navigation schemes on the market from multiple aspects of customer concern.
Handling robot vs AGV
The handling robot, as the name implies, refers to the robot used to complete the handling operation. The industrial sector generally uses wheeled drives. AGV is the abbreviation of English Automated Guided Vehicle. However, with the advancement of technology, especially the origin of the intelligent era, the introduction of concepts such as intelligent manufacturing and industrial 4.0, a variety of technologies that can be moved by autonomous vehicles and robots (including path planning, precise positioning, precise docking, intelligent scheduling, Intelligent obstacle avoidance, etc., has long been far beyond the scope of "automatic guidance", and it is not appropriate to use AGV. However, on many occasions, people still used to call it "AGV." In Bluecore Technology, R&D personnel often call it “handling robotsâ€.
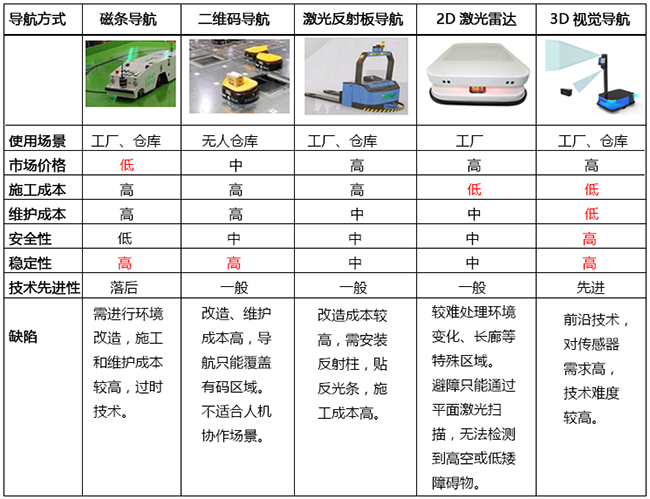
Comparison of navigation methods
There are many ways to navigate the handling machine, each with some features and usage. See the table below.
Visually unique advantages
Blue Core's unique visual navigation has clear advantages in the field of industrial handling robots (AGV).
Costly, 3D vision is used for autonomous positioning and obstacle avoidance, no need to install positioning laser radar (or only low-cost laser radar), and the maintenance cost is low;
In terms of ease of use, the path can be arbitrarily planned on the map to facilitate path switching;
In terms of safety and stability, 3D vision is adopted, information is rich, navigation is stable, and obstacle avoidance can be used to stop obstacles and obstacles, and obstacle avoidance can be avoided at a negative scale (detecting potholes), which can not be achieved by laser radar.
The Blue Core Technology R&D team has been developing deep vision systems including depth sensors and intelligent algorithms for many years. The visual system gives the robot three-dimensional sensing ability, which is embodied in the AGV, through 1. Self-developed special sensor, 2. Unique three-dimensional spatial expression, 3. Massive industrial field data, can accurately sense the surrounding environment, complete its own positioning, avoiding Barriers, navigation and other functions. In addition to industrial handling robots, deep vision systems are also reflected in product applications such as robotic grabbing, inspection, and identification.
The principle of 3D visual advantage
So how does visually remind it of its advantages?
Ancient people cloud: look through the autumn water. Today is the AI ​​era, the eyes of robots, although there is no energy of autumn water, but the basis of data, learning. In the future, robots can do their best with intelligence. A typical industrial robot can be called "blind". Why? Unparalleled ears.
Real intelligence needs to be given to the robot eyes to let the robot understand and understand the world.
From the perspective of security and stability, visual navigation has more information and more comprehensive perception of the surrounding environment.
1. Information is rich:
As the saying goes, one leaf is blind, and Taishan is not seen.
Compared to 2D laser radar, 3D vision can not only acquire contours, but also obtain texture information.
What is a dimension? A plane, representing a two-dimensional space; a room that expresses a three-dimensional space, is a three-dimensional, 3D camera that can acquire stereoscopic information within a field of view and is for three-dimensional information.
Plan view (2D) vs stereo view (3D)
2. Perceived comprehensive:
"I don't know the true face of the mountain, I am only in this mountain."
The perception of the robot will inevitably lead to blind spots. People's eyes also have blind spots, but people have binoculars, with the incomparably developed brain, the influence of blind spots is almost invisible in ordinary life. The blind spots in the machine, once neglected, may cause a safety accident. And 3D vision can reduce the blind spots of robots very well.
2D laser map vs. 3D visual map
to sum up
In general, non-visual navigation robots on the market are “scorpionsâ€. Without vision, the robot has no eyes. From the perspective of industrial automation development, the visual functions of future robots will gradually increase. Vision can now make robot (AGV) navigation more stable and safer, and it can be smarter and more complicated in the future!
This article belongs to the original article, please indicate Hangzhou Blue Core Technology Co., Ltd.
Jib cranes can be floor jib cranes and wall jib cranes. Floor Jib Crane is a floor fixed column jib crane for workshop, warehouse, wharf, etc. Wall cranes can be wall fixed jib crane and traving jib crane on wall rails, which needs no floor space and girder or beams like Bridge Crane, thus saving workshop space.

Jib crane is light crane for small capacity material handling commonly used at workshop, warehouse, wharf, production line, manufacturing production line, etc.
Jib crane capacity: 1t - 10t or custom
Lift height: 1m - 12m or custom
Work duty: A5, A6 or custom
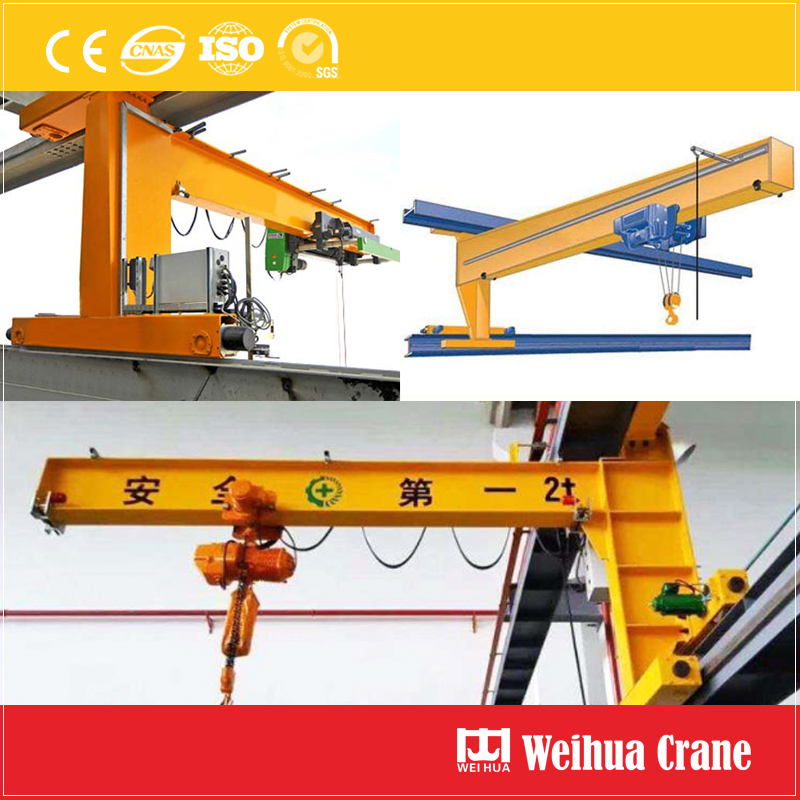

Weihua provides different jib cranes with different specifications. Just tell us your working site condition, we will provide you with the professional products and solutions. Welcome to visit us.

Jib Crane
Crane Rail,Jib Crane,Slewing Jib Crane,Floor Fixed Jib Crane
Henan Weihua Heavy Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.weihuacranefactory.com




![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)