The Mining Industry: A Comprehensive Guide
The mining industry is a vital sector that involves the discovery and extraction of naturally occurring minerals from the earth. From ancient times to today, it has played a crucial role in shaping civilizations and driving technological progress.
Throughout history, early humans used materials like clay, stones, and metals found near the surface to craft tools, weapons, and trade goods. Today, the mining industry is more advanced than ever, driven by the demand for rare elements and minerals used in modern technologies such as smartphones, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
While the environmental impact of mining remains a concern, advancements in technology have made the process more efficient, allowing miners to extract larger quantities of ore from deeper underground deposits. This has led to increased productivity and reduced the need for extensive surface disruption in many cases.
What is the Mining Industry and Why is It Important?
Mining refers to the process of extracting valuable minerals and materials from the earth. These include coal, metals, oil shale, salt, potash, gemstones, limestone, and more. The economic viability of these operations depends on factors like labor, equipment, energy, refining, and transportation costs.
The industry encompasses all stages of a mine’s life cycle—from exploration and planning to extraction, processing, and land reclamation. While non-renewable resources like natural gas and petroleum are often extracted, they are not typically considered part of the mining industry.
At an active mine, three main processes occur:
-
Mineral Extraction: This involves using either surface or underground methods to access the orebody.
-
Mineral Handling: After extraction, raw materials are separated from waste, known as tailings.
-
Mineral Processing: This step includes crushing, grinding, smelting, and refining to turn the raw material into a marketable product.
Mining is essential for providing the raw materials needed for energy production, construction, and the manufacturing of everyday consumer goods.
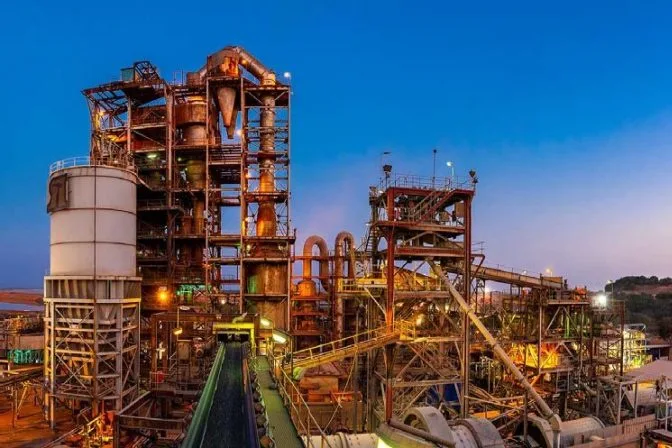 A processing plant roaster used for extractive metallurgy
A processing plant roaster used for extractive metallurgy
The Life Cycle of a Mine
The life cycle of a mine begins with prospecting, continues through extraction, and ends with land reclamation. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring both economic and environmental responsibility.
Prospecting and Discovery
Prospecting involves searching for mineral deposits using various techniques. Tools such as metal detectors, pickaxes, and electromagnetic surveys help identify potential areas. Geochemical sampling also plays a key role in detecting anomalies that may indicate valuable deposits.
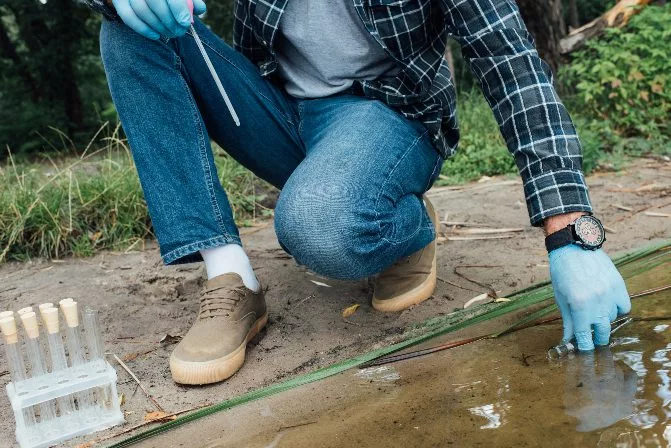 Prospector taking water samples
Prospector taking water samples
Estimating Ore Size and Value
Once a deposit is identified, its size and grade are estimated using mathematical models. These calculations help determine whether the deposit is economically viable for extraction.
Economic Feasibility Analysis
Before proceeding, mining companies evaluate several factors, including the recoverable portion of the ore, production and processing costs, market demand, and environmental considerations. Financial risks and long-term sustainability are also assessed at this stage.
Mine Development
If the project is deemed feasible, infrastructure such as processing plants, roads, and housing is built. Equipment is acquired, and the mine is prepared for operation.
Overburden Removal
Before accessing the ore, the overburden—rock and soil covering the deposit—is removed. This process requires careful planning to manage waste and minimize environmental impact.
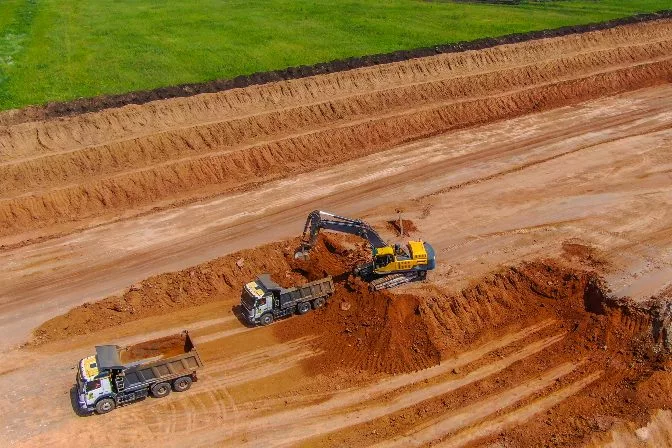 Removing overburden
Removing overburden
Waste Management
Managing waste, especially tailings, is a major challenge in mining. Tailings can be toxic and must be stored safely. However, failures in containment systems can lead to serious environmental disasters.
Mineral Processing
After extraction, the ore is processed to separate valuable minerals from waste. Techniques like crushing, grinding, and smelting are used to prepare the material for market.
Reclamation
When a mine is no longer economically viable, reclamation begins. Land is restored to its original state or repurposed for agriculture, forestry, or public use. In many countries, reclamation plans are required before a mine can operate.
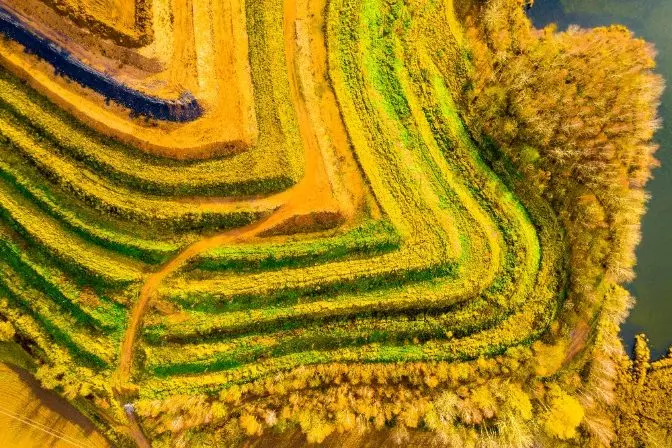 Reclamation of a surface mine
Reclamation of a surface mine
Types of Mining
Mining is broadly divided into two categories: surface mining and underground mining. Surface mining is more common due to its lower cost and easier access to deposits.
There are also different types of ore deposits, such as placer and lode deposits, which influence the choice of mining method.
Surface Mining Methods
Surface mining includes techniques like strip mining, open pit mining, quarrying, and placer mining. These methods are used when the ore is close to the surface and accessible without digging deep underground.
 An open pit surface mine
An open pit surface mine
Underground Mining Methods
Underground mining is used when the ore is too deep for surface methods. Techniques like room and pillar, retreat mining, and longwall mining are employed depending on the type of deposit and rock conditions.
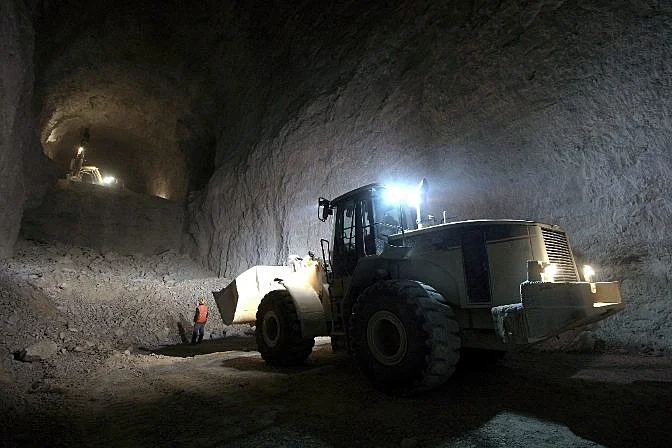 A loader clearing an underground mine drift
A loader clearing an underground mine drift
Artisanal Mining
Artisanal mining, or small-scale mining, is practiced by independent miners who use traditional tools. It is common in developing countries and provides a livelihood for millions of people. However, it often lacks regulation and poses safety and environmental risks.
Mining Industry Equipment
Mining relies on heavy machinery such as draglines, drills, loaders, and haulers. These machines are essential for moving large amounts of ore and overburden efficiently. Autonomous equipment is increasingly being used to improve safety and reduce human exposure to hazardous conditions.
 Highwall miners mine coal seams from the sides
Highwall miners mine coal seams from the sides
Mining Industry Safety
Safety is a top priority in the mining industry. Miners face risks such as rockfalls, cave-ins, and exposure to harmful substances. To mitigate these dangers, personal protective equipment (PPE) and emergency systems like refuge chambers are widely used.
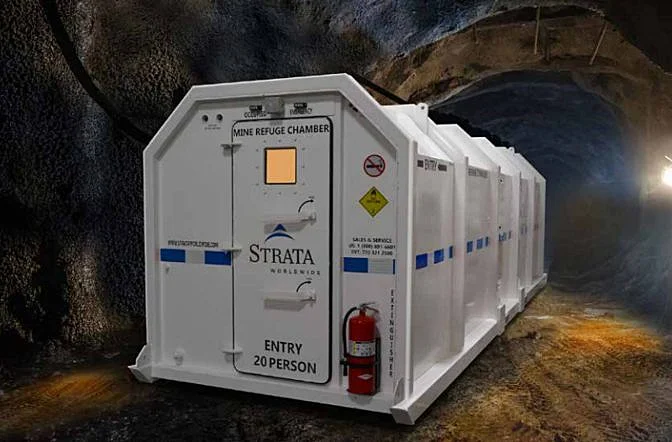

Refuge chamber in an underground mine
Environmental Impacts of the Mining Industry
Mining can have significant environmental effects, including deforestation, soil and water contamination, and loss of biodiversity. Proper planning and reclamation efforts are essential to minimize these impacts and restore affected areas.
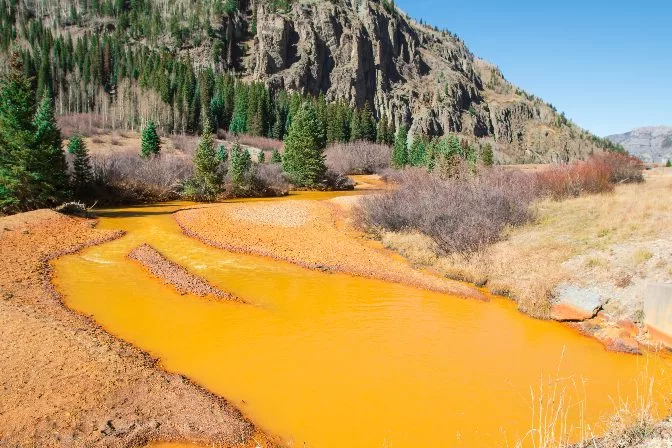 Surface water contamination
Surface water contamination
Mining Industry Regulations
Mining regulations aim to ensure safe working conditions, protect the environment, and promote responsible resource management. International standards and local laws guide the industry, though enforcement can vary significantly between regions.
Environmental Regulations
Regulations require mining companies to plan for mine closure and implement environmental management strategies. However, enforcement can be inconsistent, particularly in developing countries.
Community Regulations
Local communities often feel the effects of mining without receiving adequate benefits. Initiatives like the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) aim to increase transparency and ensure that revenues benefit local populations.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite efforts to regulate the industry, challenges remain in enforcing standards, ensuring community involvement, and addressing the needs of small-scale miners. Collaboration between governments, companies, and communities is essential to create a more sustainable and equitable mining industry.
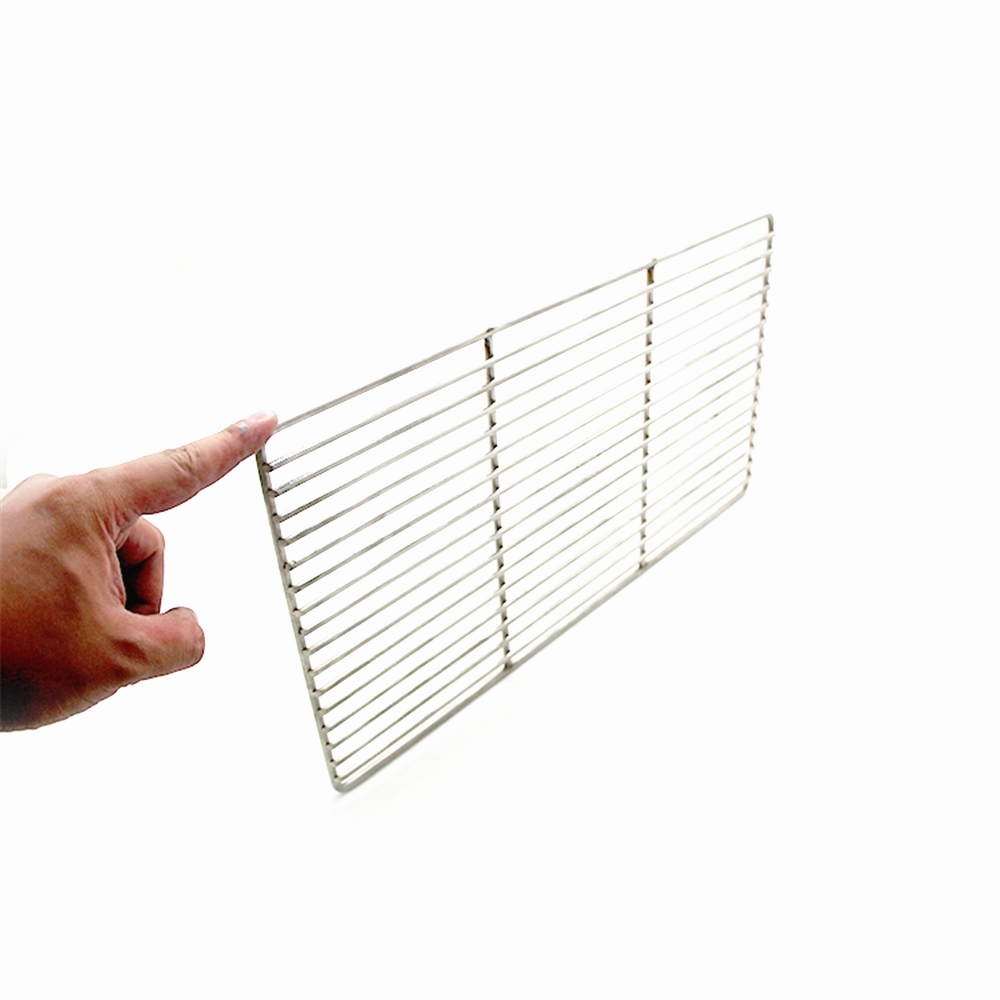
Round Shape Bbq Grill Wire Mesh
Material: Stainless Steel Wire Mesh ,Galvanized wire mesh
Weaving and features: woven and welded,High temperature resistance, no deformation, no rust, non-toxic and tasteless, easy to use; Â
Shape: Round square, arc and so on. Â
Process: flat mesh ginning mesh ,argon arc welding ,spot welding ,electrolytic polishing Â
Usage: Nowadays, the barbecue restaurants are in everywhere. More kinds of barbecue features, such as meat can have the roast mutton string, roast beef, chicken, fish, meatball, animal internal organs, such as single cascade is chicken is chicken, roast chicken wings, chicken legs, heart, etc., and even skin son can bake, corns, vegetables such as peppers, eggplant and other fruit can also be used to bake banana, so deeply love of young people on their own. Â
According to the shape is divided into: circular plane barbecue grill wire mesh, circular concave barbecue wire mesh, square plane barbecue cooking grate, square concave barbecue wire mesh. Â
According to the material is divided into: galvanized iron barbecue grill wire mesh, Â galvanized steel barbecue wire mesh , stainless steel barbecue grill wire mesh. Â
According to the handle, it is divided into: barbecue wire mesh with handle (also known as barbecue frame), barbecue wire mesh without handle. Â
Â


Â
Round Shape Bbq Grill Wire Mesh,Round Bbq Mesh,Stainless Bbq Mesh,Grid Wire Mesh
Suzhou Haoxiang Screen Stencil Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.haoxiangwiremesh.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)