Table of contents
- What is Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
- Aluminum Gauge Chart
- Popular Sheet Metal Materials
- Sheet Metal Applications
- Mild Steel Gauge Chart
- Galvanized Steel Gauge Chart
- Stainless Steel Gauge Chart
- Copper Gauge Chart
- Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Steel Sheet Metal Tolerances
- Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Thickness
- Sheet Metal Surface Finishes
- Brass Gauge Chart
- Sheet Metal Weldings
- Stainless Steel Sheet Weight
- How are Sheet Metal Gauges Used?
- Sheet Metal Advantages and Disadvantages
What is a Sheet Metal Gauge Chart?
Sheet metal gauge charts are essential tools used in the manufacturing industry to determine the thickness of metal sheets. These charts provide a direct relationship between the gauge number and the actual thickness, typically measured in millimeters or inches. A lower gauge number indicates a thicker sheet, while a higher number means a thinner one.
Understanding Aluminum Gauge Charts
The aluminum gauge chart is crucial for selecting the right material thickness for your project. Knowing the exact thickness helps in setting up the welding process and machinery. For example, some components require high strength and thus need a thicker sheet, while others can function with a thinner one. This ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Choosing the correct gauge not only enhances the durability of the final product but also reduces production and shipping costs. Using an aluminum gauge chart allows you to make informed decisions about material selection based on your specific needs.
Aluminum Gauge Chart (in mm and inches)
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 3.665 | 3.264 | 2.906 | 2.588 | 2.305 | 2.053 | 1.628 | 1.291 |
| Inches | 0.1443 | 0.1285 | 0.1144 | 0.1019 | 0.09074 | 0.08081 | 0.06408 | 0.05082 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | – |
| MM | 1.024 | 0.812 | 0.644 | 0.511 | 0.405 | 0.321 | 0.255 | – |
| Inches | 0.0403 | 0.03196 | 0.02535 | 0.0201 | 0.01594 | 0.01264 | 0.01003 | – |
Common Sheet Metal Materials
Several materials are commonly used in sheet metal fabrication, including stainless steel, pre-plated steel, cold rolled steel, copper, brass, and aluminum. Each has unique properties that make them suitable for different applications:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, available in 300 and 400 series.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and highly malleable, ideal for various industrial uses.
- Copper/Brass: Conductive and durable, often used in electrical and decorative applications.
- Pre-plated Steel: Offers enhanced corrosion resistance and is used in construction and automotive industries.
Applications of Sheet Metal
Sheet metal is widely used across multiple industries due to its versatility and durability. Some common applications include:
- Architectural designs
- Structural components
- Housings and enclosures
- Manufacturing parts
- Cabinets and furniture
- Construction and automation systems
Mild Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge no. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.554 | 4.175 | 3.797 | 3.416 | 3.038 | 2.656 | 1.897 |
| Inches | 0.1793 | 0.1644 | 0.1495 | 0.1345 | 0.1196 | 0.1046 | 0.0747 |
| Gauge no. | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 |
| MM | 1.518 | 1.214 | 0.911 | 0.759 | 0.607 | 0.454 | 0.378 |
| Inches | 0.0598 | 0.0478 | 0.0359 | 0.0299 | 0.0239 | 0.0179 | 0.0149 |
Galvanized Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge no. | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.269 | 3.891 | 3.51 | 3.1318 | 2.753 | 1.9939 | 1.6129 |
| Inches | 0.1681 | 0.1532 | 0.1382 | 0.1233 | 0.1084 | 0.0785 | 0.0635 |
| Gauge no. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 |
| MM | 1.31 | 1.005 | 0.853 | 0.701 | 0.551 | 0.474 | 0.398 |
| Inches | 0.0516 | 0.0396 | 0.0336 | 0.0276 | 0.0217 | 0.0187 | 0.0157 |
Stainless Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge No | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.365 | 3.968 | 3.571 | 3.175 | 2.778 | 1.984 | 1.587 |
| Inches | 0.17187 | 0.15625 | 0.14062 | 0.125 | 0.10937 | 0.07812 | 0.0625 |
| Gauge No | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 |
| MM | 1.27 | 0.9525 | 0.7937 | 0.635 | 0.476 | 0.396 | 0.3175 |
| Inches | 0.05 | 0.0375 | 0.03125 | 0.025 | 0.01875 | 0.01562 | 0.0125 |
Copper Gauge Chart
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.572 | 4.191 | 3.759 | 3.404 | 3.048 | 2.769 | 2.108 | 1.651 |
| Inches | 0.18 | 0.165 | 0.148 | 0.134 | 0.12 | 0.109 | 0.083 | 0.065 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | |
| MM | 1.245 | 0.889 | 0.711 | 0.559 | 0.457 | 0.356 | 0.305 | |
| Inches | 0.049 | 0.035 | 0.028 | 0.022 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.012 |
Sheet Metal Fabrication Overview
Sheet metal fabrication involves a range of processes such as bending, cutting, punching, forming, welding, finishing, and inspection. Each step plays a vital role in shaping and assembling the final product:
- Bending: Done using a press brake to create desired angles.
- Cutting: Includes methods like shearing, laser cutting, and plasma cutting.
- Punching: Performed using a punch press or CNC machine.
- Forming: Involves stamping, rolling, and deep drawing.
- Welding: Techniques like MIG and TIG ensure secure joints.
- Finishing: Painting, coating, and plating protect against corrosion.
- Inspection: Ensures dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
Steel Sheet Metal Tolerances
| Gauge | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal [in] | 0.1345 | 0.1196 | 0.1046 | 0.0747 | 0.0598 | 0.0478 | 0.0359 | 0.0299 | 0.0239 | 0.0179 | 0.0149 | |
| Max | Size [in] | 0.1405 | 0.1256 | 0.1106 | 0.0797 | 0.0648 | 0.0518 | 0.0389 | 0.0329 | 0.0269 | 0.0199 | 0.0169 |
| Min | Size [in] | 0.1285 | 0.1136 | 0.0986 | 0.0697 | 0.0548 | 0.0438 | 0.0329 | 0.0269 | 0.0209 | 0.0159 | 0.0129 |
Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Thickness
| Gauge | 12 | 11 | 24 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.109" | 2.78mm | 0.120" | 3.05 mm | 0.025" | 0.64 mm | 0.063" | 1.59mm |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.009 | ± 0.23mm | ± 0.005 | ± 0.003 | ± 0.08mm | ± 0.006 | ± 0.15mm |
| Gauge | 14 | 20 | 18 | 22 |
| Thickness | 0.078" | 1.98mm | 0.038" | 0.95mm | 0.050" | 1.27mm | 0.031" | 0.79 mm |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.007 | ± 0.18mm | ± 0.004 | ± 0.10mm | ± 0.005 | ± 0.13mm | ± 0.004 | ± 0.10mm |
Sheet Metal Surface Finishes
- Annealing
- Galvanised
- Tinning
- Anodising
- Tempering
Brass Gauge Chart
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 3.665 | 3.264 | 2.906 | 2.588 | 2.305 | 2.053 | 1.628 | 1.291 |
| Inches | 0.1443 | 0.1285 | 0.1144 | 0.1019 | 0.09074 | 0.08081 | 0.06408 | 0.05082 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | |
| MM | 1.024 | 0.812 | 0.644 | 0.511 | 0.405 | 0.321 | 0.255 | |
| Inches | 0.0403 | 0.03196 | 0.02535 | 0.0201 | 0.01594 | 0.01264 | 0.01003 |
Sheet Metal Welding Techniques
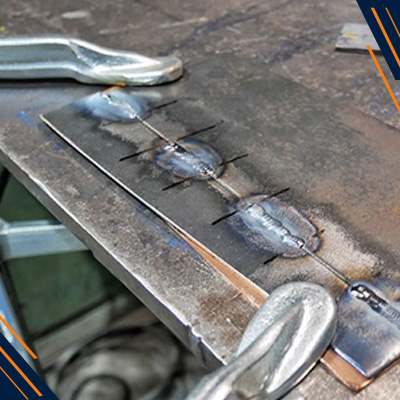

MIG Welding

TIG Welding

Laser Welding

Stick Welding

GAS Welding

Plasma Arc welding
Stainless Steel Sheet Weight
| Weight Per Stainless Steel Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight KG/M2 | 1.44 | 1.6 | 1.76 | 1.92 | 2.16 | 2.24 | 2.56 | 3.04 | 3.52 | 4 | 4.48 | 5.04 | 6 | 7.04 | 8 | 9.04 | 10 | 72 | 12 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.5 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 1 | .1.13 | 1.25 | 1.38 | 1.5 | |
| Size(mm) | 2500 X 1250 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 11 | 12.5 | 14 | 15.75 | 18.75 | 22 | 25 | 28.25 | 31.25 | 34.5 | 37.5 |
| 2000 X 1000 | 2.88 | 3.2 | 3.52 | 3.84 | 4.32 | 4.48 | 5.12 | 6.08 | 7.04 | 8 | 8.96 | 10.08 | 12 | 14.08 | 16 | 18.08 | 20 | 22.03 | 24 | |
| 3000 X 1500 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 36 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 54 | |
| Weight KG/M2 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 1.75 | 2 | 2.25 | 2.5 | 2.75 | 3 | 3.25 | 3.5 | 3.75 | 4 | 4.25 | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 6.5 | 7 | 7.5 | 8 | |
| Size(mm) | 2500 X 1250 | 43.75 | 50 | 56.25 | 62.5 | 68.75 | 75 | 81.25 | 87.5 | 93.75 | 100 | 106.25 | 112.5 | 125 | 137.5 | 150 | 162.5 | 175 | 187.5 | 200 |
| 2000 X 1000 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | 68 | 72 | 80 | 88 | 96 | 104 | 112 | 120 | 128 | |
| 3000 X 1500 | 63 | 72 | 81 | 90 | 99 | 108 | 117 | 126 | 135 | 144 | 153 | 162 | 180 | 198 | 216 | 234 | 252 | 270 | 288 | |
How are Sheet Metal Gauges Used?
Sheet metal gauges are used to specify the thickness of a sheet, which varies depending on the material. For instance:
- 18-gauge steel = 0.0478 inches (1.214 mm)
- 18-gauge aluminum = 0.0403 inches (1.023 mm)
The same gauge number can represent different thicknesses based on the type of material used. Understanding this helps in choosing the right gauge for specific applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sheet Metal
Advantages
- Durable
- High Accuracy
- Versatility
- Malleable
- Rapid Prototyping
- Lightweight
- High Strength
- Cost-Effective
Disadvantages
- Cost for Complex Designs
- Aesthetic Appearance
- High tooling and equipment costs
Luohe Letone Hydraulic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.litonghose.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)